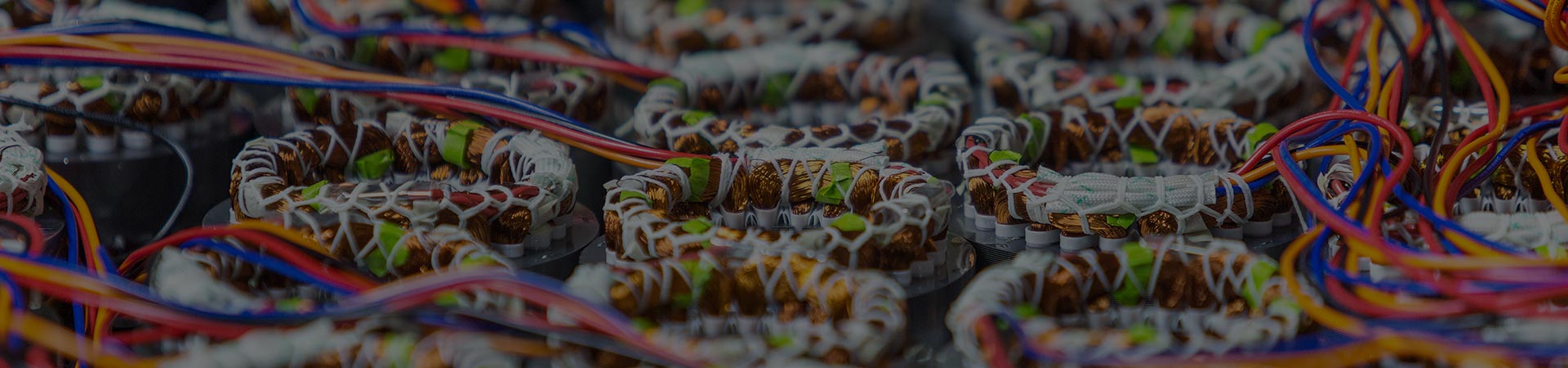
A three-phase AC motor is an electric motor that operates on a three-phase power supply. Let's explore the definition, advantages, applications, structure, and characteristics of a three-phase AC motor, as well as how to install and use it.
Definition:
A three-phase AC motor is an electric motor that runs on a three-phase electrical power system, where three alternating currents of equal magnitude and frequency are supplied. It is widely used in various industrial and commercial applications due to its efficiency and reliability.
Advantages:
High Efficiency: Three-phase AC motors are known for their high efficiency, converting electrical energy into mechanical energy with minimal energy loss.
Constant Power Output: These motors provide a constant power output, ensuring smooth and consistent operation.
Higher Starting Torque: Three-phase motors offer higher starting torque, making them suitable for applications that require high initial power to start heavy loads.
Compact and Lightweight: These motors are generally more compact and lighter compared to single-phase motors of similar power rating.
Reduced Maintenance: Three-phase AC motors have a simpler construction and fewer moving parts, resulting in reduced maintenance requirements and increased reliability.
Applications:
Industrial Machinery: Three-phase AC motors are extensively used in various industrial machinery such as pumps, compressors, conveyors, mixers, fans, and blowers.
HVAC Systems: They are employed in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems to power air handlers, chillers, and cooling towers.
Manufacturing Equipment: Three-phase motors drive machines and equipment used in manufacturing processes, including machine tools, conveyors, and robotics.
Agricultural Applications: These motors are used in agricultural machinery like irrigation pumps, grain conveyors, and milking machines.
Commercial Applications: They are found in commercial applications such as elevators, escalators, refrigeration systems, and water treatment plants.
Structure and Characteristics:
The structure of a three-phase AC motor typically includes:
Stator: The stationary part of the motor that houses the stator windings. It generates a rotating magnetic field when energized by three-phase power.
Rotor: The rotating part of the motor that interacts with the stator's magnetic field, inducing rotor currents and producing rotational motion.
Bearings: Allow smooth rotation of the rotor and reduce friction.
Housing: Encloses and protects the internal components of the motor.
Terminal Box: Contains the connection terminals for the power supply and control wiring.
Installation and Usage:
Power Supply: Connect the motor to a suitable three-phase power supply, ensuring correct phase sequence and voltage compatibility.
Mounting: Securely mount the motor to a suitable base or frame using appropriate brackets or fasteners.
Wiring: Follow the manufacturer's wiring diagram and connect the motor leads to the corresponding terminals in the control panel.
Starting and Control: Depending on the motor's design, use appropriate starting methods such as direct-on-line (DOL), star-delta, or soft starters. Use motor control devices such as contactors, relays, and motor protection devices for efficient operation.
Maintenance: Regularly inspect the motor for signs of wear, clean it to remove dust and debris, and lubricate the bearings as per the manufacturer's recommendations.
Safety Precautions: Prioritize safety by wearing appropriate personal protective equipment, ensuring the motor is properly grounded, and following electrical safety guidelines.
Always refer to the manufacturer's instructions and guidelines specific to the three-phase AC motor you are using for detailed installation, wiring, and maintenance instructions. Seek assistance from a qualified electrician or technician if needed.